This application note presents programming techniques for reading an external voltage by employing bitstream continuous calibration in order to create a simple, inexpensive 8-bit 1 analog to digital converter with an input range of 0-5V. This implementation uses the SX's internal interrupt feature to allow background operation of the code as a virtual peripheral, and uses the Parallax demo board, taking advantage of Parallax' SX demo software user interface and UART features to allow the SX to communicate simply and directly with a personal computer via a serial RS232C port.

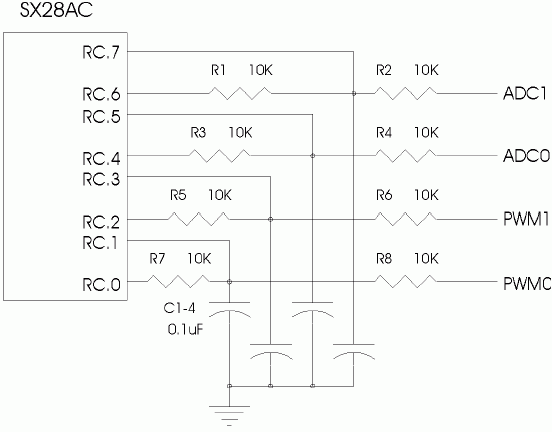
Figure 1 - Parallax demo board ADC/PWM circuit diagram
;****************************************************************************** ; Virtual Peripheral: Analog to Digital Converters ; ; ; Length: 36 bytes (total) ; Authors: Chip Gracey, President, Parallax Inc. ; modified by Craig Webb, Consultant to Scenix Semiconductor, Inc. ; Written: 97/03/10 to 98/6/03 ; ;****************************************************************************** ; ;****** Assembler directives ; ; uses: SX28AC, 2 pages of program memory, 8 banks of RAM, high speed osc. ; operating in turbo mode, with 8-level stack & extended option reg. ; DEVICE pins28,pages2,banks8,oschs DEVICE turbo,stackx,optionx ID 'ADCS' ;program ID label RESET reset_entry ;set reset/boot address ; ;******************************* Program Variables *************************** ; ; Port Assignment: Bit variables ; adc0_out_pin EQU rc.4 ;ADC0 input pin adc0_in_pin EQU rc.5 ;ADC0 output/calibrate pin adc1_out_pin EQU rc.6 ;ADC1 input pin adc1_in_pin EQU rc.7 ;ADC1 output/calibrate pin ; ; ;****** Register definitions (bank 0) ; org 8 ;start of program registers main = $ ;main bank ; temp ds 1 ;temporary storage byte ds 1 ;temporary UART/I2C shift reg. flags DS 1 ;program flags register ; delay1 DS 1 ;temporary delay variable delay2 DS 1 ;temporary delay variable ; org 50h ;bank2 variables analog = $ ;pwm and ADC bank ; port_buff ds 1 ;buffer - used by all adc0 ds 1 ;adc0 - value adc0_count ds 1 ; - real-time count adc0_acc ds 1 ; - accumulator adc1 ds 1 ;adc1 - value ;adc1_count ds 1 ; - real-time count adc1_acc ds 1 ; - accumulator ; ; int_period = 163 ;period between interrupts ; ;**************************** INTERRUPT CODE ******************************* ; ; Note: The interrupt code must always originate at 0h. ; Care should be taken to see that any very timing sensitive routines ; (such as adcs, etc.) are placed before other peripherals or code ; which may have varying execution rates (like the UART, for example). ; interrupt ORG 0 ;interrupt starts at 0h ; ; ;***** Virtual Peripheral: Bitstream Analog to Digital Converters ; ; These routines allow an 8-bit value to be calculated which corresponds ; directly (within noise variation limits) with the voltage (0-5V) present ; at the respective adc port input pins. These routines are timing critical ; and must be placed before any variable-execution-rate code (like the UART, ; for example). The currently enabled routine (version A) has been optimized ; for size and speed, and RAM register usage, however a fixed execution rate, ; yet slightly larger/slower routine (version B) is provided in commented ; (disabled) form to simplify building other timing-critical virtual ; peripheral combinations (i.e. that require fixed rate preceeding code). ; Note: if version B is selected, version A must be disabled (commented) ; ; Input variable(s) : adc0,adc0_acc,adc0_count,adc1,adc1_acc,adc1_count ; Output variable(s) : pwm port pins ; Variable(s) affected : port_buff, pwm0_acc, pwm1_acc ; Flag(s) affected : none ; Size (version A) : 9 bytes + 7 bytes (per pwm) ; + 2 bytes shared with adc code (see below) ; Size (version B) : 6 bytes + 10 bytes (per pwm) ; + 2 bytes shared with pwm code (see below) ; Timing (turbo) ; version A : 2 cycles shared with pwm code (see below) + ; (a) [>99% of time] 11 cycles + 4 cycles (per adc) ; (b) [<1% of time] 9 cycles + 7 cycles (per adc) ; version B : 6 cycles + 10 cycles (per adc) ; + 2 cycles shared with pwm code (see below) ; :set_analog bank analog ;switch to adc/pwm bank clr port_buff ;clear pwm/adc port buffer :adcs mov w,>>rc ;get current status of adc's not w ;complement inputs to outputs and w,#%01010000 ;keep only adc0 & adc1 or port_buff,w ;store new value into buffer :update_RC mov rc,port_buff ;update cap. discharge pins ; ; VERSION A - smaller, quicker but with variable execution rate ; :adc0 sb port_buff.4 ;check if adc0 triggered? INCSZ adc0_acc ;if so, increment accumulator INC adc0_acc ; and prevent overflowing DEC adc0_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' :adc1 sb port_buff.6 ;check if adc1 triggered INCSZ adc1_acc ;if so, increment accumulator INC adc1_acc ; and prevent overflowing DEC adc1_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' INC adc0_count ;adjust adc0 timing count JNZ :done_adcs ;if not done, jump ahead :update_adc0 MOV adc0,adc0_acc ;samples ready, update adc0 :update_adc1 MOV adc1,adc1_acc ; update adc1 :clear_adc0 CLR adc0_acc ; reset adc0 accumulator :clear_adc1 CLR adc1_acc ; reset adc1 accumulator ; ; <end of version A> ; ; VERSION B - fixed execution rate ; ;*** The "adc1_count" register definition in the analog bank definition ;*** section must be enabled (uncommented) for this routine to work properly ; ;:adc0 sb port_buff.4 ;check if adc0 triggered ; INCSZ adc0_acc ;if so, increment accumulator ; INC adc0_acc ; and prevent overflowing ; DEC adc0_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' ; mov w,adc0_acc ;load W from accumulator ; inc adc0_count ;adjust adc0 timing count ; snz ;are we done taking reading? ; mov adc0,w ;if so, update adc0 ; snz ; ; clr adc0_acc ;if so, reset accumulator ; ;:adc1 sb port_buff.6 ;check if adc1 triggered ; INCSZ adc1_acc ;if so, increment accumulator ; INC adc1_acc ; and prevent overflowing ; DEC adc1_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' ; mov w,adc1_acc ;load W from accumulator ; inc adc1_count ;adjust adc1 timing count ; snz ;are we done taking reading? ; mov adc1,w ;if so, update adc1 ; snz ; ; clr adc1_acc ;if so, reset accumulator ; ; <end of version B> ; :done_adcs mov w,#-int_period ;interrupt every 'int_period' clocks :end_int retiw ;exit interrupt ; ;****** End of interrupt sequence ; ;***************************** SUBROUTINES ********************************* ; ;***************************** MAIN PROGRAM CODE ****************************** ; ; ORG 100h ; ; Program execution begins here on power-up or after a reset ; reset_entry clr rc ;initialize port RC mov !rc,#%10101010 ;Set RC in/out directions mov m,#$D ;set input levels mov !rc,#0 ; to cmos on port C mov m,#$F ;reset mode register CLR FSR ;reset all ram starting at 08h :zero_ram SB FSR.4 ;are we on low half of bank? SETB FSR.3 ;If so, don't touch regs 0-7 CLR IND ;clear using indirect addressing IJNZ FSR,:zero_ram ;repeat until done mov !option,#%10011111 ;enable rtcc interrupt ; ; Main Program Loop ; :loop MOV W,adc0 ;get adc0 value ; ; <program code goes here> ; JMP :loop ;back to main loop ; ;*************** END ;End of program code
The circuit is a simple resistor capacitor network on each adc port pin (see figure 1). Essentially, the program code calculates the charge vs. discharge rates of the capacitor, according to the voltage (0-5V) applied to the corresponding adc input. Port pins RC.5 and RC.7 are both inputs which trigger when the capacitor is half charged. This is because, using mode register function 0Dh in the initialization section of the main program code, port pin input and outputs on port RC are set CMOS levels.
The interrupt code segment uses the bitstream continuous calibration approach to calculate the capacitor charge/discharge timing. The method is a rather unique one, which uses one port to monitor the capacitor level, and another as an output to charge and discharge the capacitor to keep it hovering at the input trigger level. The charging and discharging times depend on the voltage being applied to the corresponding adc input, and hence by measuring the charge time vs. (charge + discharge) time ratio, we can determine the voltage present at the adc input. The resolution of such a method is proportional to the calibration frequency, and due to circuit noise, the last few bits ( + 1 or 2 LSB's) must usually be thrown away.
Using adco as our example, the adc routine keeps count in the adc0_acc register of the number of times the adc input (port pin RC.5) is triggered high during 256 passes through the interrupt (the count of the number of passes being kept in the adc0_count register). The ratio of these two values gives the proportion of Vcc present at the adc0 input.
adc0_acc / adc0_count = Vadc0_nput / Vdd
| * Note: the original SX demo code erroneously returns an adc value of 0 for input voltages ³ Vdd |
In this implementation, a sample is taken as soon as adc0_count rolls over from 255 to 0, whereupon the value contained in adc0_acc is copied to adc0. This value, ranging from 0-255 *, directly corresponds to an input voltage of 0-5 volts, with a value of 0 representing 0 volts and a value of 0FFh representing 5V. It should be noted that with no input voltage present the input floats around (or very near to) a value of 7Fh, though slight offsets may result due to variations between what should be equal values for the resistors R3 and R4.
The resistor capacitor combination shown allows sampling of the incoming signal by the bitstream continuous calibration method described above, yet it also draws current from the input source in order to maintain the calibration at 0.5V dd . The effect of this is equivalent to having the input source connected through R4 (in this case a 10kW resistor) to 2.5 volts, so current drain considerations on the input source should be kept in mind.
| 2 Due to Nyquist's theorem, useful information can only be obtained for frequencies £ half of the sampling (or, in this case, the calibration) frequency. |
For adc0, SX port pin RC.6 is essentially acting like a auto-calibrating pulse width modulation output which keeps the capacitor at 0.5V cc using real-time feedback from port pin RC.7. This method for analog to digital conversion is effective for inputs whose highest frequency component is lower than half2 of the lowest frequency component of the calibrating pwm signal.
| 3 With an input voltage just under 5 volts, the pwm calibration output will only toggle high for 1 out of every 256 interrupt passes. With the input at (or over) 5 volts, the calibration output will remain low. For an input voltage slightly over 0 volts, the pwm calibration output will toggle low only 1 of every 256 passes, and with the input at (or below) 0V, the calibration output will remain high. |
The length of the pwm cycle varies, depending upon the voltage of the input, but the worst case is a pwm that toggles only once every 256 interrupt passes 3.
We can calculate the period between interrupt passes as follows:
| The interrupt is triggered each time the RTCC rolls over (counts past 255 and restarts at 0). By loading the OPTION register with the appropriate value, the RTCC count rate is set to some division of the oscillator frequency (in this case they are equal), which is the external 50 MHz crystal in this case. At the close of the interrupt sequence, a predefined value is loaded into the W register using the RETIW instruction, which determines the period of the interrupt in RTCC cycles. |
period (sec) = mode * prescaler * RETIW value / osc. frequency, where mode=1 (turbo) or =4 (normal)
So, for the worst case of 256 interrupt passes, at a crystal frequency of 50 MHz, in turbo mode, with a prescaler of 1, and with an RETIW value of 163, the lowest frequency present in the pwm signal is:
frequencypwm_min = 1 / period * 256 = 50 MHz / (1 * 1 * 163 * 256 ) = 1.2 kHz
| 4 In practice, even signals at or near this frequency will not sample with 8 bits of resolution. |
By this we can see that the adc will be able to monitor signals at or below4 fadc_max = 1.2kHz / 2 = 600 Hz.
| 5 For signals that vary within a minimal range about the 1/2Vdd calibration point, higher frequencies may be successfully monitored. |
At frequencies above5 this, not only will the adc begin to provide inaccurate information, but there will also be an increasing current drain on the incoming signal as the impedance to ground of the RC combination decreases.
Since timing is critical for accurate readings, all efforts should be made to make sure that any code executed in the interrupt prior to the adc code section maintains a uniform execution rate at all times. This can be done by placing it before any varying-execution-rate, state-dependent code (it should always come before the UART, for instance).
The Parallax demo board is designed so that port pins pwm0 and pwm1 can be swapped for adc's simply by adjusting the program code to remove the pwm interrupt section, adding code to the :adcs section such that adc2 and adc3 use port RC pins for pwm0 and pwm1, respectively, and by adjusting the register definitions appropriately. An example of the code follows:
analog = $ ;adc bank ; port_buff ds 1 ;buffer - used by all adc0 ds 1 ;adc0 - value adc0_acc ds 1 ; - accumulator adc1 ds 1 ;adc1 - value adc1_acc ds 1 ; - accumulator adc2 ds 1 ;adc2 - value adc2_acc ds 1 ; - accumulator adc3 ds 1 ;adc3 - value adc3_acc ds 1 ; - accumulator adc_count ds 1 ;adc calibration count ... ; ; <all pwm code removed> ; :adcs MOV W,>>RC ;get current status of adc's NOT W ;complement inputs to outputs AND W,#%01010000 ;keep only adc0 & adc1 OR port_buff,W ;store new value into buffer MOV RC,port_buff ;update cap. discharge pins :adc0 SB port_buff.4 ;check if adc0 triggered? INCSZ adc0_acc ;if so, increment accumulator INC adc0_acc ; and prevent overflowing DEC adc0_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' :adc1 SB port_buff.6 ;check if adc1 triggered INCSZ adc1_acc ;if so, increment accumulator INC adc1_acc ; and prevent overflowing DEC adc1_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' :adc2 SB port_buff.0 ;check if adc2 triggered INCSZ adc1_acc ;if so, increment accumulator INC adc1_acc ; and prevent overflowing DEC adc1_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' :adc3 SB port_buff.2 ;check if adc3 triggered INCSZ adc1_acc ;if so, increment accumulator INC adc1_acc ; and prevent overflowing DEC adc1_acc ; by skipping second 'INC' INC adc_count ;adjust adc's timing count JNZ :done_adcs ;if not, jump ahead MOV adc0,adc0_acc ;update adc0 MOV adc1,adc1_acc ;update adc1 MOV adc2,adc2_acc ;update adc2 MOV adc3,adc3_acc ;update adc3 CLR adc0_acc ;reset adc0 accumulator CLR adc1_acc ;reset adc1 accumulator CLR adc2_acc ;reset adc2 accumulator CLR adc3_acc ;reset adc3 accumulator :done_adcs ...