© 2000 Scenix Semiconductor, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 23 -
www.scenix.com
SX18AC/SX20AC/SX28AC/SX18AC75/SX20AC75/SX28AC75
9.2 External RC Mode
The external RC oscillator mode provides a cost-effective
approach for applications that do not require a precise
operating frequency. In this mode, the RC oscillator fre-
quency is a function of the supply voltage, the resistor (R)
and capacitor (C) values, and the operating temperature.
In addition, the oscillator frequency will vary from unit to
unit due to normal manufacturing process variations. Fur-
thermore, the difference in lead frame capacitance
between package types also affects the oscillation fre-
quency, especially for low C values. The external R and
C component tolerances contribute to oscillator fre-
quency variation as well.
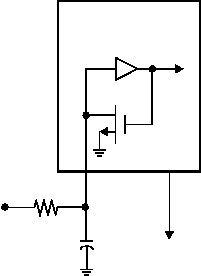
Figure 9-3 shows the external RC connection diagram.
The recommended R value is from 3kW to 100kW. For R
values below 2.2kW, the oscillator may become unstable,
or may stop completely. For very high R values (such as
1 MW), the oscillator becomes sensitive to noise, humid-
ity, and leakage.
Although the oscillator will operate with no external
capacitor (C = 0pF), it is recommended that you use val-
ues above 20 pF for noise immunity and stability. With no
or small external capacitance, the oscillation frequency
can vary significantly due to variation in PCB trace or
package lead frame capacitances.
9.3 Internal RC Mode
The internal RC mode uses an internal oscillator, so the
device does not need any external components. At 4
MHz, the internal oscillator provides typically +/–8%
accuracy over the allowed temperature range. The inter-
nal clock frequency can be divided down to provide one
of eight lower-frequency choices by selecting the desired
value in the FUSE Word register. The frequency range is
from 31.25 KHz to 4 MHz. The default operating fre-
quency of the internal RC oscillator may not be 4 MHz.
This is due to the fact that the SX device requires trim-
ming to obtain 4 MHz operation. The parts shipped out of
the factory are not trimmed. The device relies on the pro-
gramming tool provided by the third party vendors to sup-
port trimming.
10.0 REAL TIME CLOCK
(RTCC)/WATCHDOG TIMER
The device contains an 8-bit Real Time Clock/Counter
(RTCC) and an 8-bit Watchdog Timer (WDT). An 8-bit
programmable prescaler extends the RTCC to 16 bits. If
the prescaler is not used for the RTCC, it can serve as a
postscaler for the Watchdog Timer. Figure 10-1 shows
the RTCC and WDT block diagram.
10.1 RTCC
RTCC is an 8-bit real-time timer that is incremented once
each instruction cycle or from a transition on the RTCC
pin. The on-board prescaler can be used to extend the
RTCC counter to 16 bits.
The RTCC counter can be clocked by the internal instruc-
tion cycle clock or by an external clock source presented
at the RTCC pin.
To select the internal clock source, bit 5 of the OPTION
register should be cleared. In this mode, RTCC is incre-
mented at each instruction cycle unless the prescaler is
selected to increment the counter.
To select the external clock source, bit 5 of the OPTION
register must be set. In this mode, the RTCC counter is
incremented with each valid signal transition at the RTTC
pin. By using bit 4 of the OPTION register, the transition
can be programmed to be either a falling edge or rising
edge. Setting the control bit selects the falling edge to
increment the counter. Clearing the bit selects the rising
edge.
The RTCC generates an interrupt as a result of an RTCC
rollover from 0FF to 000. There is no interrupt pending bit
to indicate the overflow occurrence. The RTCC register
must be sampled by the program to determine any over-
flow occurrence.
Figure 9-3. RC Oscillator Mode
Vdd
R
C
Internal
Circuitry
OSC2
OSC1
N
~
SX Device