© 1999 Scenix Semiconductor, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 20 -
www.scenix.com
SX18AC / SX20AC / SX28AC
9.0
OSCILLATOR CIRCUITS
The device supports several user-selectable oscillator
modes. The oscillator modes are selected by program-
ming the appropriate values into the FUSE Word register.
These are the different oscillator modes offered:
9.1
XT, LP or HS modes
In XT, LP or HS, modes, you can use either an external
resonator network or an external clock signal as the
device clock.
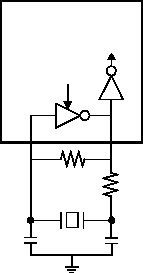
To use an external resonator network, you connect a
crystal or ceramic resonator to the OSC1/CLKIN and
OSC2/CLKOUT pins according to the circuit configura-
tion shown in Figure 9-1. A parallel resonant crystal type
is recommended. Use of a series resonant crystal may
result in a frequency that is outside the crystal manufac-
turer specifications.
Bits 0, 1 and 5 of the FUSE register (FOSC1:FOSC2) are
used to configure the diffrent external resonator/crystal
oscillator modes. These bits allow the selection of the
appropriate gain setting for the internal driver to match
the desired operating frequency. If the XT, LP, or HS
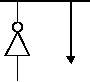
mode is selected, the OSC1/CLKIN pin can be driven by
an external clock source rather than a resonator network,
as long as the clock signal meets the specified duty
cycle, rise and fall times, and input levels (Figure 9-2). In
this case, the OSC2/CLKOUT pin should be left
open.The recommended target values for the external
component values are available at Scenix website..
9.2
External RC Mode
The external RC oscillator mode provides a cost-effective
approach for applications that do not require a precise
operating frequency. In this mode, the RC oscillator fre-
quency is a function of the supply voltage, the resistor (R)
and capacitor (C) values, and the operating temperature.
In addition, the oscillator frequency will vary from unit to
unit due to normal manufacturing process variations. Fur-
thermore, the difference in lead frame capacitance
between package types also affects the oscillation fre-
quency, especially for low C values. The external R and
C component tolerances contribute to oscillator fre-
quency variation as well.
Figure 9-3 shows the external RC connection diagram.
The recommended R value is from 3kW to 100kW. For R
values below 2.2kW, the oscillator may become unstable,
or may stop completely. For very high R values (such as
1 MW), the oscillator becomes sensitive to noise, humid-
ity, and leakage.
Although the oscillator will operate with no external
capacitor (C = 0pF), it is recommended that you use val-
ues above 20 pF for noise immunity and stability. With no
or small external capacitance, the oscillation frequency
can vary significantly due to variation in PCB trace or
package lead frame capacitances.
In the external RC mode, the OSC2/CLKOUT pin pro-
vides an output frequency, which the input frequency
divided by four.
9.3
Internal RC Mode
The internal RC mode uses an internal oscillator, so the
device does not need any external components. At 4
MHz, the internal oscillator provides +/–8% accuracy
over the allowed temperature range. The internal clock
frequency can be divided down to provide one of eight
lower-frequency choices by selecting the desired value in
the FUSE Word register. The frequency range is from
31.25 KHz to 4 MHz. The default operating frequency of
the internal RC oscillator may not be 4 MHz. This is due
LP: Low Power Crystal
XT: Crystal/Resonator
HS: High Speed Crystal/Resonator
RC: External Resistor/Capacitor
Internal Resistor/Capacitor
Figure 9-1. Crystal Operation (or Ceramic Resonator)
(HS, XT or LP OSC Configuration)
SX Device
RF
XTAL
OSC2
OSC1
C1
C2
Internal
Circuitry
SLEEP
RS
Figure 9-2. External Clock Input Operation
(HS, XT or LP OSC Configuration)
Externally
Generated Clock
OSC1
OSC2
Open
SX Device