IP2022 Data Sheet
www.ubicom.com
79
6.0 In-System Programming
The IP2022 provides a dedicated serial interface for in-
system programming (ISP) of the flash program memory
and configuration block. ISP allows designers to
incorporate a small connector which can be used to
interface to a device programmer for programming or
reprogramming the IP2022 after it has been soldered to a
circuit board.
The interface used for in-system programming (ISP) and
in-system debugging (ISD) is compatible with the SPI
serial interface protocol. Whenever possible, a standard
connector should be incorporated in the system design for
in-system
debugging
and
programming.
The
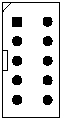
recommended connector layout for the ISD/ISP interface
is shown in Figure 6-1. The connector is a male 10-pin
connector with 100-mil pin spacing, whose pin
assignments are listed in Table 6-1. The connector is
keyed to prevent backward insertion.
Figure 6-1 ISD/ISP Connector
Signal levels on the connector are LVTTL-compatible.
The target system provides the TSCK, TSI, TRST, and
TSS signals with 10K ohm pullup resistors.
For more information about the ISD/ISP interface and the
interaction between the debugger/programmer and the
target system, see the IP2022 User’s Manual.
Table 6-1 Connector Pin Assignments
Pin
Name
Description
1
KEY
Key (not a signal)
2
TSS
Target Slave Select—Active-low sig-
nal which enables the IP2022 to com-
municate on the SPI bus. Connect to
pin 1 on the IP2022.
3
GND
Ground
1
515-053.eps
3
5
7
9
2
4
6
8
10
4
TSCK
Target Data Clock—Serial clock. Con-
nect to pin 2 on the IP2022.
5
OSC
Target Clock Oscillator—If the debug-
ger/programmer is capable of supply-
ing an OSC clock for the target
system, then this clock must be con-
figurable so that it can be disabled to
prevent it from interfering with the tar-
get system (i.e. the OSC clock output
is placed in a high-impedance state).
6
Reserved Reserved
7
TRST
Target Reset—The target system may
use the TRST signal to reset the
entire system, to reset only the
IP2022, or it may ignore the TRST sig-
nal. The debugger/programmer may
provide a 100-ms system reset signal
(TRST) to the target system. If sup-
ported, the TRST output must be an
open-collector driver to accommo-
date other sources of reset in the tar-
get system. The minimum source
requirement for this driver is 6 mA.
The debugger/programmer should not
detect or be reset by the TRST signal
being driven low by the target system.
There is no requirement that the
IP2022 is connected to the TRST sig-
nal, so the debugger/programmer
cannot assume that the IP2022 has
been reset if the target system pulls
the TRST pin low.
8
TSI
Target Serial Input—Sampled on the
rising edge of TSCK. Connect to pin 3
on the IP2022.
9
VDD
Power. 2.3 - 3.6V (optional)
10 TSO
Target Serial Output—Driven by the
IP2022 after the falling edge of
TSCK. Connect to pin 4 on the
IP2022.
Table 6-1 Connector Pin Assignments (continued)
Pin
Name
Description