IP2022 Data Sheet
www.ubicom.com
23
3.7.5
Disabled Resources
If a peripheral is disabled and its interrupt flag is cleared,
the peripheral does not have the ability to set an interrupt
flag. The interrupt flag, however, is still a valid source of
interrupt (If software sets an interrupt flag, the
corresponding interrupt enable bit is set, and the GIE bit
is set, then the CPU will be interrupted whether or not the
peripheral is enabled or disabled).
If a peripheral is disabled inside the ISR, then its interrupt
flag must be cleared to prevent an undesired interrupt
from being taken when the ISR completes or when GIE is
enabled (enabling nested interrupts - see Section 3.7.2).
3.7.6
Wakeup
Recovery from SLEEP mode to normal execution is
possible from these sources:
•
External interrupts (i.e. Port B interrupts)
•
Real-time timer interrupts
•
Watchdog timer overflow reset
•
Brown-out voltage reset
•
RST external reset
The first two sources listed do not reset the chip, so
program execution continues from where it was stopped
after the interrupt is serviced. The last three sources reset
the chip, so software must perform all of its reset
initialization tasks to recover. This usually requires
additional time, as compared to recovery through an
interrupt. If a port B or Real Time Timer interrupt occurs
during system clock stop mode, the INTSPD register will
be copied to the SPDREG register, the ISR will be
executed, then mainline code will resume execution at the
instruction after the speed command that caused the
clock to stop.
3.8
Reset
There are five sources of reset:
•
Power-On Reset (POR)
•
Brown-Out Reset (BOR)
•
Watchdog Reset
•
External Reset (from the RST pin)
•
Target Reset (from the debugging interface)
Each of these reset conditions causes the program
counter to branch to the reset vector at the top of the
program memory (word address 0xFFF0 or byte address
0x1FFE0).
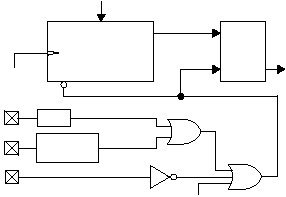
The IP2022 incorporates a Power-On Reset (POR)
detector that generates an internal reset as DVdd rises
during power-up. Figure 3-11 is a block diagram of the
reset logic. It includes a 10-bit startup timer and a reset
latch. The startup timer controls the reset time-out delay.
The reset latch controls the internal reset signal. On
power-up, the reset latch is set (CPU held in reset), and
the startup timer starts counting once it detects a valid
logic high signal on the RST pin. Once the startup timer
reaches the end of the timeout period, the reset latch is
cleared, releasing the CPU from reset.
Note: RST pulse width must be at least 10ms.
Figure 3-11 On-Chip Reset Circuit Block Diagram
10-Bit Asynchronous
Ripple Counter
(Start-Up
Timer)
R
S
Q
Brown-Out
Detection
RST
DVDD
Watchdog Timer
Overflow
Watchdog
RC Clock
(~15.6KHz)
Time-Out
Internal
Reset Signal
(active high)
POR
Power-On Reset
515-023c.eps
Clear
For RST, Tool Reset or Watchdog = WUDX2:0 (FUSE0)
For POR or BOR = 1025
AVDD