56
www.ubicom.com
IP2022 Data Sheet
the RTEOS bit should be set to ensure the CPU can
reliably read the RTTMR register.
If the value in the RTTMR register needs to be used by the
CPU and the Real-Time Timer is required to function
when the system clock is set to RTCLK or off, then
software must change the RTEOS bit when changing the
system clock source. To read the RTTMR register when
the system clock is not synchronous to the RTCLK, the
RTEOS bit must be set to ensure reliable operation.
Before the system clock is changed to RTCLK or turned
off, the RTEOS bit must be clear (i.e. RTCLK not
oversampled) for the Real-Time Timer to continue to
function.
5.4
Multi-Function Timers (T1 and T2)
The IP2022 contains two independent 16-bit multi-
function timers, called T1 and T2. These versatile,
programmable timers reduce the software burden on the
CPU in real-time control applications such as PWM
generation, motor control, triac control, variable-
brightness display control, sine-wave generation, and
data acquisition.
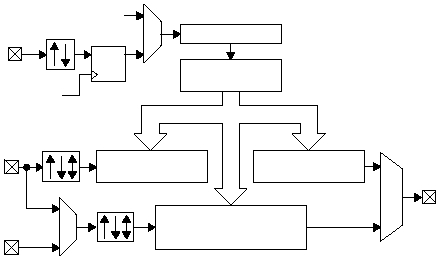
Each timer consists of a 16-bit counter register supported
by a dedicated 16-bit capture register and two 16-bit
compare registers. The second compare register can also
serve as capture register. Each timer may use up to four
external pins: TxCPI1 (Capture Input), TxCPI2 (Capture
Input), TxCLK (Clock Input), TxOUT (Output). These pins
are multiplexed with general-purpose I/O port pins. The
port direction register has priority over the timer
configuration, so the port direction register must be
programmed appropriately for each of these four signals
if their associated timer functions are used.
Figure 5-7 is a block diagram showing the registers and
I/O pins of one timer. Each timer is based on a 16-bit
counter/timer driven by a 15-bit prescaler. The input of the
prescaler can be either the system clock or an external
clock signal which is internally synchronized to the system
clock. The counter cannot be directly written by software,
but it may be cleared by writing to the TxRST bit in the
TxCTRL register.
Each timer should be enabled before its interrupt is
enabled.
Figure 5-7 Multifunction Timer Block Diagram
515-005.eps
TxCPI1
TxCAP1H/TxCAP1L
Register
TxOUT
TxCMP1H/TxCMP1L
Register
TxCLK
D Q
TxCPI2
TxCAP2H/TxCAP2L
or TxCMP2H/TxCMP2L
Register
TxCNTH/TxCNTL
Register
15-Bit Prescaler
System
Clock
System
Clock