© 2005 Ubicom, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 33 -
www.ubicom.com
SX20AC/SX28AC
15.12 Subroutine Operation
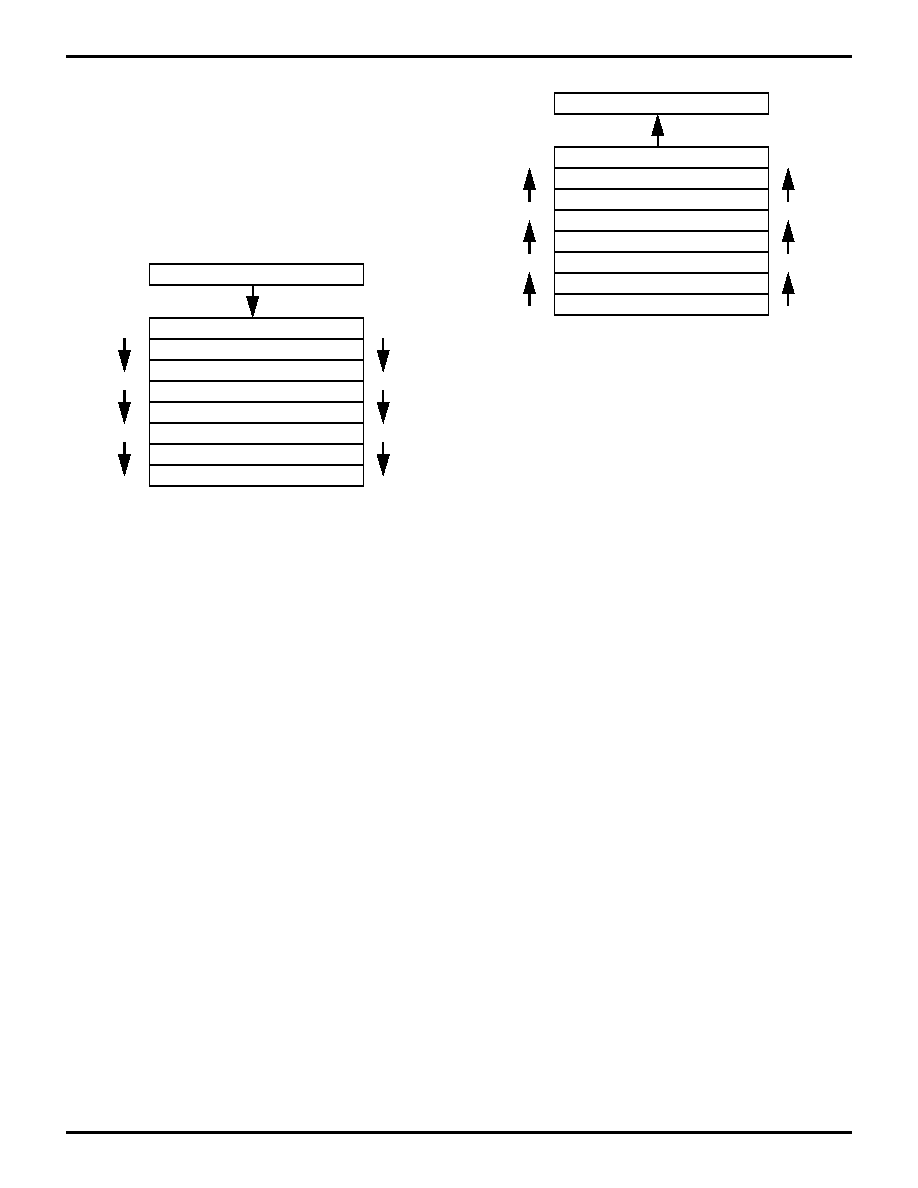
15.12.1 Push Operation
When a subroutine is called, the return address is
pushed onto the subroutine stack. Specifically, each
address in the stack is moved to the next lower level in
order to make room for the new address to be stored.
Stack 1 receives the contents of the program counter.
Stack 8 is overwritten with what was in Stack 7. The con-
tents of stack 8 are lost.
15.12.2 Pop Operation
When a return instruction is executed the subroutine
stack is popped. Specifically, the contents of Stack 1 are
copied into the program counter and the contents of each
stack level are moved to the next higher level. For exam-
ple, Stack 1 receives the contents of Stack 2, etc., until
Stack 7 is overwritten with the contents of Stack 8. Stack
8 is left unchanged, so the contents of Stack 8 are dupli-
cated in Stack 7.
15.13 Comparison and Conditional Branch
Instructions
The instruction set includes instructions such as DECSZ
fr (decrement file register and skip if zero), INCSZ fr
(increment file register and skip if zero), SNB bit (bit test
file register and skip if bit clear), and SB bit (bit test file
register and skip if bit set). These instructions will cause
the next instruction to be skipped if the tested condition is
true. If a skip instruction is immediately followed by a
PAGE or BANK instruction (and the tested condition is
true) then two instructions are skipped and the operation
consumes three cycles. This is useful for conditional
branching to another page where a PAGE instruction pre-
cedes a JMP. If several PAGE and BANK instructions
immediately follow a skip instruction then they are all
skipped plus the next instruction and a cycle is consumed
for each.
PC<10:0>
STACK 1
STACK 2
STACK 3
STACK 4
STACK 5
STACK 6
STACK 7
STACK 8
PC<10:0>
STACK 1
STACK 2
STACK 3
STACK 4
STACK 5
STACK 6
STACK 7
STACK 8

