Circuit explanation
for DC motor speed controller
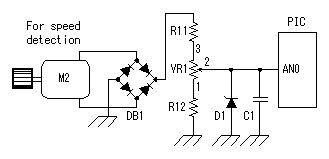 This is the circuit which inputs the control voltage which was created by the turning of the motor in PIC. The input voltage to PIC is converted by A/D converter. Changed voltage is used for the PWM function of the CCP to control the motor drive. At the circuit this time, a small motor is used as the generator to detect the number of rotations of the motor. The input voltage (the control voltage) to PIC is changed by the fluctuation of the number of rotations of the motor. The other way can be used to detect the number of rotations of the motor. It is need to change control voltage to proportional to the number of rotations of the motor. PIC controls the drive electric current of the motor for the control voltage to become a regulation value. When the revolution of the motor slows down, i.e. control voltage goes down, the drive electric current of the motor is increased and number of rotations is raised. When the control voltage reaches a regulation value, an drive electric current at the point is held. Oppositely, when the number of rotations of the motor is high, i.e. the control voltage is high, the drive electric current of the motor is reduced and number of rotations is lowered. When the control voltage reaches a regulation value, an drive electric current at the point is held. This is the circuit which inputs the control voltage which was created by the turning of the motor in PIC. The input voltage to PIC is converted by A/D converter. Changed voltage is used for the PWM function of the CCP to control the motor drive. At the circuit this time, a small motor is used as the generator to detect the number of rotations of the motor. The input voltage (the control voltage) to PIC is changed by the fluctuation of the number of rotations of the motor. The other way can be used to detect the number of rotations of the motor. It is need to change control voltage to proportional to the number of rotations of the motor. PIC controls the drive electric current of the motor for the control voltage to become a regulation value. When the revolution of the motor slows down, i.e. control voltage goes down, the drive electric current of the motor is increased and number of rotations is raised. When the control voltage reaches a regulation value, an drive electric current at the point is held. Oppositely, when the number of rotations of the motor is high, i.e. the control voltage is high, the drive electric current of the motor is reduced and number of rotations is lowered. When the control voltage reaches a regulation value, an drive electric current at the point is held.DB1 is used to make not conscious of the polarity of the motor. When never making a mistake in the connection, to use isn't necessary. When the voltage of the motor for the speed detection is small, it is better not to put. D1 is used to protect PIC when the voltage of the detection motor is high. C1 is to make bypass the noise of the detection motor. VR1 is the variable resistor to set the number of rotations of the main motor. The input voltage of PIC becomes low when bringing VR1 close to the side 1 and PIC increases the drive electric current of the motor. That is, the revolution of the motor rises. The input voltage of PIC becomes high when bringing VR1 close to the side 3 and PIC reduces the drive electric current of the motor. That is, the revolution of the motor slows down. For the details of the CCP, refer to "CCP feature of PIC16F873". 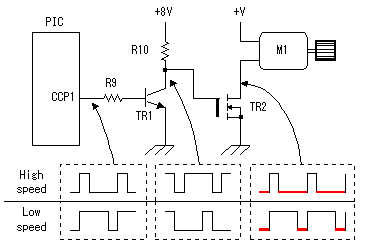 The PWM(Pulse Width Modulation) function of PIC is used for the electric current control to drive a motor.PWM can change the duty of the pulse to output into CCP1 by the data. When the time which is made the H level of the pulse of CCP1 is short, the time of ON (the L level) becomes long in TR2. That is, the drive electric current of the motor increases. Oppositely, when the H level time of the pulse of CCP1 is long, the ON time of TR2 becomes short and the drive electric current of the motor decreases. The PWM(Pulse Width Modulation) function of PIC is used for the electric current control to drive a motor.PWM can change the duty of the pulse to output into CCP1 by the data. When the time which is made the H level of the pulse of CCP1 is short, the time of ON (the L level) becomes long in TR2. That is, the drive electric current of the motor increases. Oppositely, when the H level time of the pulse of CCP1 is long, the ON time of TR2 becomes short and the drive electric current of the motor decreases.The duty of the pulse of CCP1 is controlled in the voltage (the control voltage) which was taken in with the control voltage input circuit. When the control voltage is higher than the regulation value, the H level time of the CCP1 pulse is made long and the number of rotations of the motor is lowered. When the control voltage is lower than the regulation value, the H level time of the CCP1 pulse is made short and the number of rotations of the motor is raised. I used N-channel MOS FET for the drive of the motor. The P-channel MOS FET can be used, too. In the case, the duty control of the CCP1 pulse becomes opposite. It becomes low-speed when the H level of the pulse is short and when long, it becomes high-speed. The way of connecting between the motor and the FET becomes opposite. In this case, the power of the transistor for the FET drive should be connected with the source terminal of P-FET. 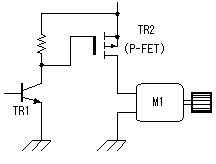 For the details of MOS FET, refer to "MOS FET". For the details of the CCP, refer to "CCP feature of PIC16F873". 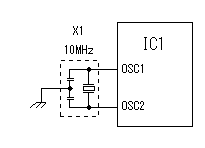 I am using 10-MHz resonator. There is not directly relation but it is related with the taking-in period with control voltage, the period of the motor driving pulse to the number of rotations of the motor. 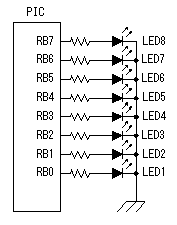 LEDs are made to light up to monitor the drive situation of the motor. 3 bits of higher ranks of the control data of PWM are used for the lighting-up of LEDs. In the condition that a motor isn't driven, all LEDs are turned off. The number of the lighting-up is increased in the order from LED1 as the drive electric current increases. When the motor is in the maximum drive condition, all LEDs become a lighting-up condition. At the equipment this time, the LED of the bar type with seven LEDs is used. The circuit can control eight LEDs. However, at the equipment this time, LED1 isn't used and seven LEDs from LED2 to LED8 are used. An LED is lit up when RBx is H level. 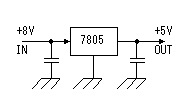 3 terminal regulator is used to get the operating voltage for PIC. The about 70-mA electric current flows when seven LEDs are lit up at the same time. I used a 1 A-type regulator for the safety. |